In the first two installments we explored distortions that created catastrophes from our imagination and another that was the least helpful filter ever then we looked at how the polarization of thought impacts us and the dramatic limitation of “mind-reading.” Now, it’s on to Emotional Reasoning and, one of my personal favorites, Should Statements.
- Catastrophizing
- The Mental Filter
- Black-and-White Thinking
- Mind-Reading
- Emotional Reasoning
- ‘Shoulding’
- Personalization
- False Permanence
- Blaming
- Magical Thinking
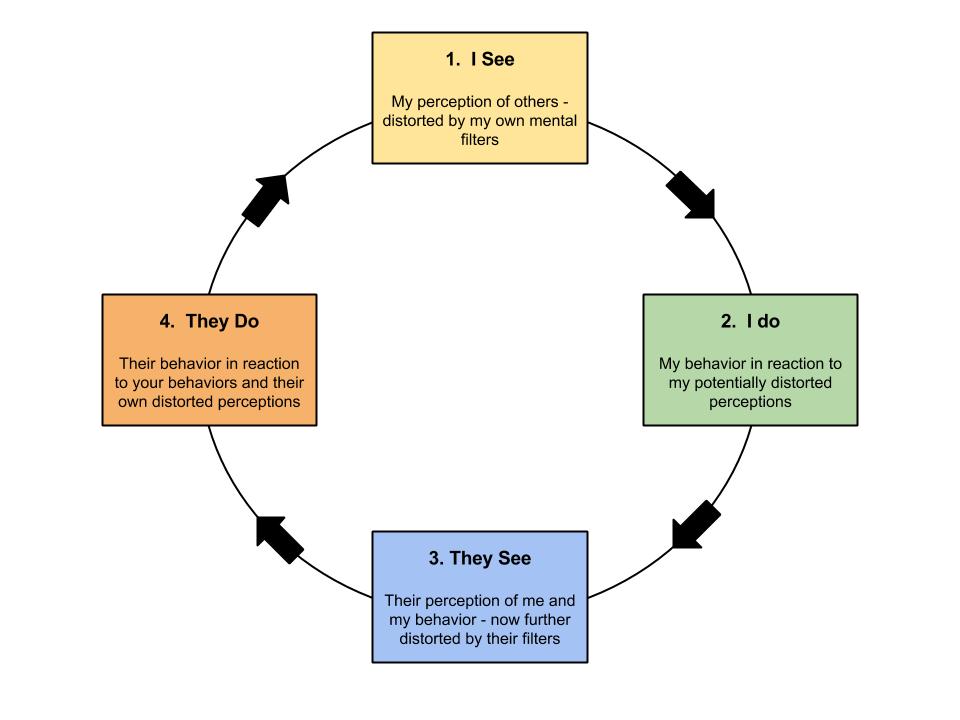
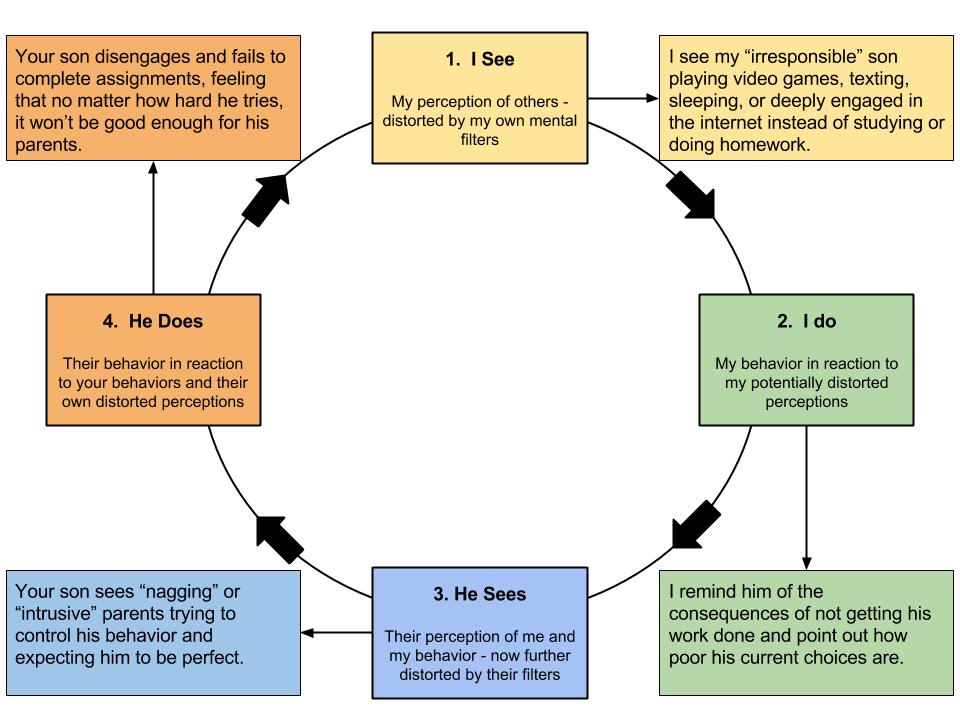
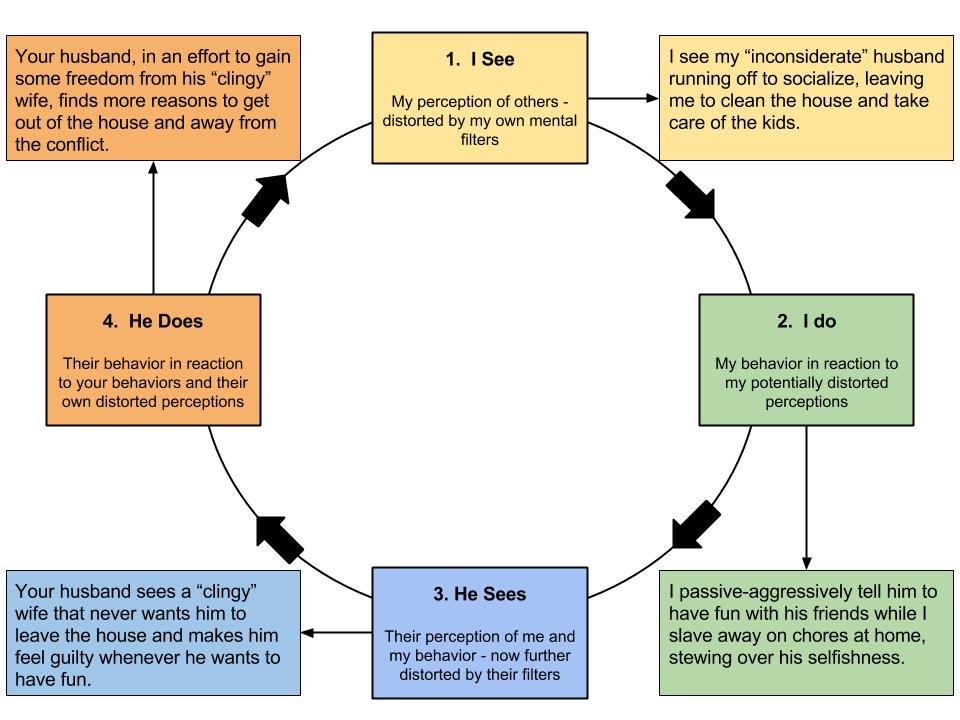
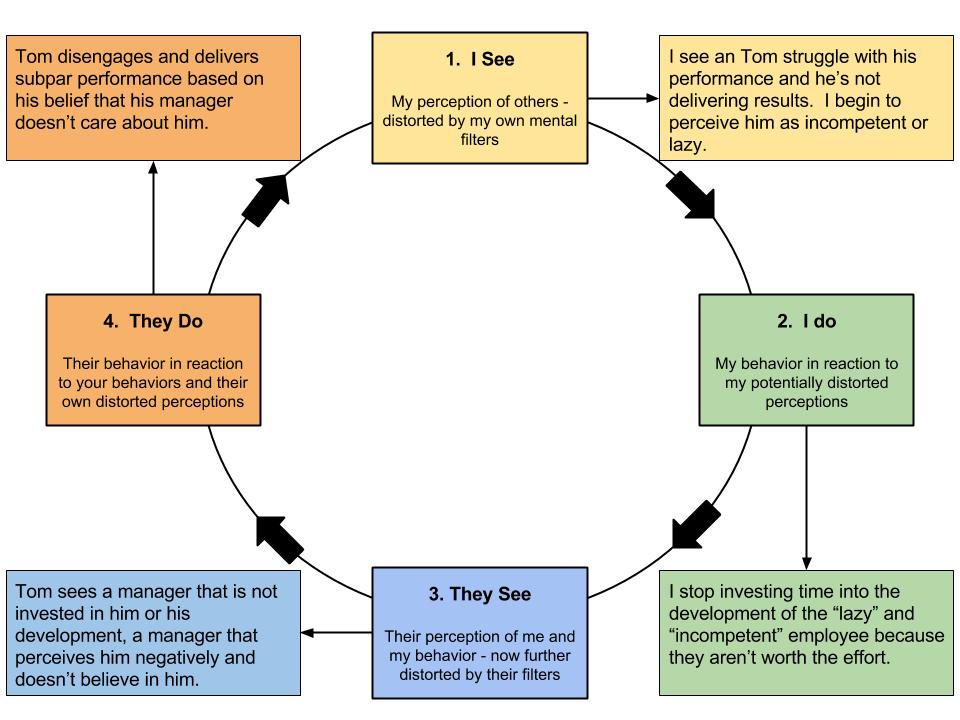
Let me remind you – as you begin to challenge these distortions, for effective change, take the time to write down the specific unhelpful thoughts as you recognize them and write down the alternative thinking patterns that will set you on the path to healthier ways of perceiving your experiences. You’ll see overlap in how these patterns feed into one another, each one making the others a little easier to believe, creating a seemingly unified (albeit distorted) vision of life. Don’t be fooled.
- Emotional Reasoning: When reality becomes distorted by Emotional Reasoning, we’ve allowed emotions to be in the driver’s seat while we sit in the back, eyes closed and hoping for the best. Our emotional experience defines the entire experience. Some examples are personal and internal – “I felt anxious before/during/after the presentation, so it must have been horrible.” Notice the evaluation of the situation is based entirely on the emotion rather than the actual execution of the presentation. While emotional reasoning applied to performances can drastically reduce your ability to feel successful, when it’s applied to broader concepts it can be even more harmful. “I feel worthless, so I must have done done something wrong or I must not be doing enough” “I feel sad, so it’s going to be a bad day…It will be impossible to enjoy anything.” This type of reasoning can be equally destructive in interpersonal relationships. “I feel hurt, so Johnny must have done something wrong.” Again, you’ll notice that the evaluation has nothing to do with what’s being evaluated; it’s based solely on the emotional experience.
Challenging Emotional Reasoning: In every example above, the disconnect between the evaluation and the target of evaluation was clear, and it’s much harder to see that distinction when you’re the one in the situation. Therefore, to successfully change this distortion, one of the first things we want to do is increase awareness and acceptance of emotions WITHOUT EVALUATION. The practice involves identifying and describing emotions…then stopping the narrative. “I feel hurt..my muscles are tense; I’m hot; I’m crying.” There is no need to judge yourself, your emotions, or anybody else when you’re hurt. Identify it, describe it, and then decide what action you want to take (if any). “I’m hurt. I feel it in my whole body. I want to exercise because when I’m hurt, taking care of myself is even more important.” Another strategy for dealing with emotional reasoning is to preemptively define success without depending on emotions. Setting a goal like “I’m going to be super relaxed during my presentation.” means your success is based exclusively on your emotions (which you have limited control over). When you define success by other more behavioral factors (finishing within the time limit, maintaining eye contact, etc.), you can be anxious and successful. Whenever you recognize your emotions leading you down a path of judgement, criticism, or any other form of distorted thinking, step away from the situation, acknowledge and accept the emotions, then proceed according to your values instead of listening exclusively to your emotions.
- Should Statements: Why are “should” statements my favorite? Two main reasons. First, we use “should” so ubiquitously that everyone has multiple opportunities to catch this pattern of distorted thinking on a daily basis. Secondly, there are really straight forward ways of challenging these phrases. So, what is a “should” statement. Any time you use “should” you’re committing a small act of harm to your mental well-being. The more powerful the “should,” the more destructive it becomes. How can such a common word be so detrimental? It has to do with the subtle impact our language has on our beliefs and emotions. Every time we use the word “should” there is some amount of judgment and criticism that go along with it. “He should be doing his homework.” means that there is something wrong with him for not doing it, and he would be doing it “right” if he were doing his homework. “I should exercise more” carries the same subtle judgment – “I’m bad because of the amount of exercise I’m currently doing and I would be good if I exercised more” Whether it’s directed at yourself or someone else, that judgment and criticism, overtime, can be toxic. Another component that makes “should” harmful is the battle it consistently establishes. It’s a battle that sets you up to lose every time you use the word. “Should” implies that reality is not acceptable – it argues that reality is wrong. Reality, in any given moment, can’t be altered, and our past certainly can’t be changed. “I should have…” only serves to function as a critical (and largely unnecessary) judgment of something that cannot be changed. (Could, would, ought, and need are close cousins to “should” and create similar harmful effects).
One last problem with “shoulding.” It allows the user to feel righteous and therefore avoid responsibility for being an active participant in changing. Proclaiming how things “should” be, frequently leaves people feeling justified in their own inaction. “She should know better.” “He shouldn’t have said that.” “They should stop.” “This shop should be open.” The onus is placed firmly on the proverbial “other” to be responsible for change, greatly reducing the possibility of finding effective solutions.
Challenging “Should” Statements: Once it’s in your head that “should” is causing harm, you’ll start to recognize all the places you use it, directed at yourself and others. Replacing it can be difficult, even though it’s relatively a simple process of word replacement. In most circumstances, swapping “should” for “I want” is enough. “I want him to do his homework” and “I want to exercise more” moves away from judgment and toward healthy identification of preferences. Stick with the facts here. Instead of “should,” simply describe the circumstances. “I exercised for 20 minutes two days this week. I want to exercise for 30 minutes on three days next week” Stay solution oriented and future oriented. “Shoulds” can also be an indicator that expectations or boundaries have not been assertively communicated (or consequences haven’t been effectively applied) with others or clear goals haven’t been set for yourself.
If you find yourself “shoulding” take the time to write down what you want and make a plan for how to get it. Look at what you can do differently to help things go the way you want them to go. When “shoulds” are applied retroactively, a slightly different approach can be used. Rather than judging the past, focus on the future. “Next time I will…” or “In the future I want to…” This reframes the potential solution, making it less about a harsh judgment and verbal punishment, and more about productive action.
Next we’ll cover Personalization and False Permanence.